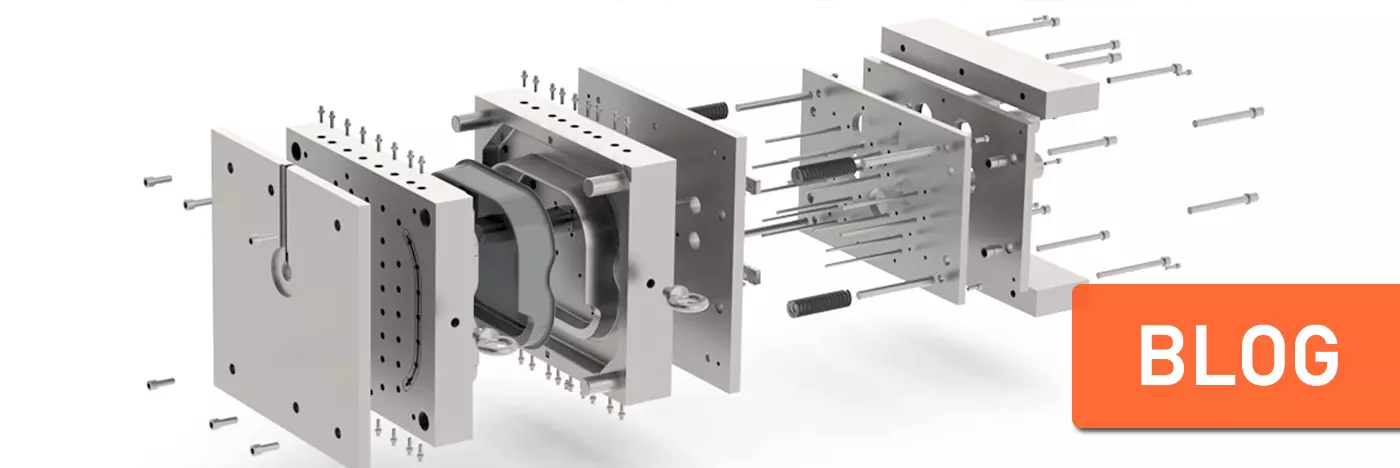
The Top Quality Injection Mold Components In Canada

Our world is full of plastic creations, like complicated medical tools and the hard shell of your phone. But have you ever thought about how these complex forms are made? The secret is in a fantastic engineering technique: injection molding. This method needs the exact cooperation of different injection mold components, each one important in changing hot, liquid plastic into the desired shape. Injection molds themselves are amazing, but let's look more closely at the top quality injection mold components in Canada that make them work:
1. Mold Base (Clamp Plates)
This is one of the core injection mold components, the very base of the mold, sometimes called clamp plates. It's responsible for holding everything together, like the stage where the action occurs.
- Purpose: These sturdy plates keep the mold's two parts (one that moves and one that doesn't) secure. They're usually made of top-notch steel to endure the tough pressure that comes with injecting.
- Thoughts on Design: Designers of Injection Mold have to think about lots of factors, like size and complexity of the piece, needed injection pressure, and type of molding machine when they're design the mold base. They also must ensure the mold halves align correctly for exact part copying.
- Picking a Mold Manufacturer: Choosing injection mould manufacturers who know how to craft the mold bases that work best for your specific project is important. They need the right machines and knowledge to tackle the size and strictness of the base.
2. Cavities and Cores
Molds are pretty cool. Want to know why? It's because of the cavities and cores. These guys shape melted plastic into whatever you want. Picture this: cavities are just like molds of your desired part. When molten plastic fills up the cavity, it solidifies and takes the shape of the cavity.
Cores, though, are the sculptors of the inside stuff, like holes or cutouts. Designing these cavities and cores isn't a walk in the park. It needs super careful attention. When designing, folks factor in things like how the material might shrink, what kind of finish the surface needs and special features or shapes that need a bit extra work to pop out.
Here's another thing: if you are going to make molds, you better know your stuff. Injection Mold Designers should have packing skills and machinery that lets them carve out tricky cavities and cores with pinpoint accuracy. They often calls in multi-axis CNC machining and polishing moves to get the exact detail and finish they want.
3. Runners and Sprues
The paths for molten plastic within a mold are called Runners and Sprues. Picture these channels like temporary roads. The sprue's role is to move molten plastic from the machine's nozzle into the mold. Then, runners spread out from the sprue. These offshoots shuttle the plastic to the mold's pockets. When it comes to design, it's important to balance.
Runner and sprue designs should make the plastic flow well but not be wasteful. So, Injection Mould Designers tweak runner size and layout. Their goal is to fill pockets properly and use less material for creating these paths. There's an optional approach called Hot Runner Systems. With these, runners stay molten, so there's no need for an extra sprue. Also, they create less waste. However, Hot Runner Systems tend to be complex and pricey to use.
4. Cooling System
Quick chilling is among critical injection mold components for properly hardening plastic inside the mold.
- Role: The mold base contains a built-in channel network, carrying a cooling agent (water or oil). This agent moves around, soaking up the mold cavity's heat. It cools and hardens the molten plastic faster, leading to quicker cycles and increased production.
- Design Factors: Where the cooling channels and their design are key for even cooling of the part. Those who design Injection Molds carefully locate these routes. They make sure the plastic cools at a steady pace to lower the chance of twisting or internal tension.
- Manufacturing Skills: Those who make Injection Molds should know how to insert effective cooling systems inside the mold base. This might require complex drilling or milling methods to carve out the detailed channel network.
5. Ejection System
After the plastic hardens, you must take the completed piece from its mold. Here's where the ejection system fits in. It comprises special ejector pins or plates positioned inside the mold. As the mold splits open, these pins or plates give the plastic piece a nudge out, turning it easier to remove it. The way we design the ejection system considers the shape of the part. We also balance it carefully to stop it from misshaping or getting damaged when ejected.