- Mould Manufacturer
- Tooling
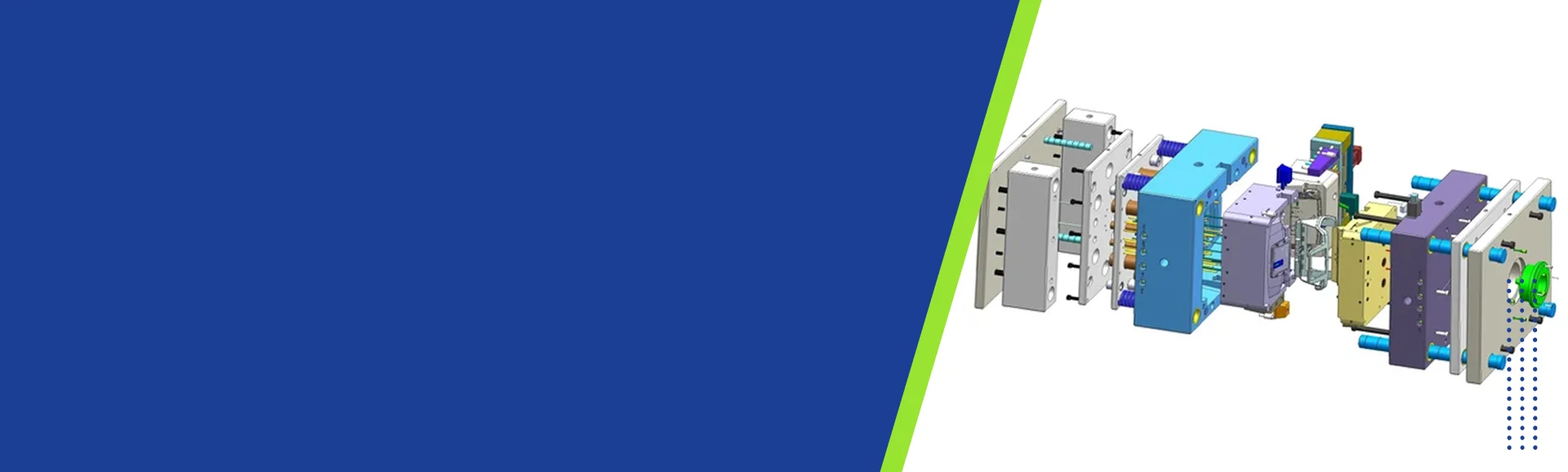
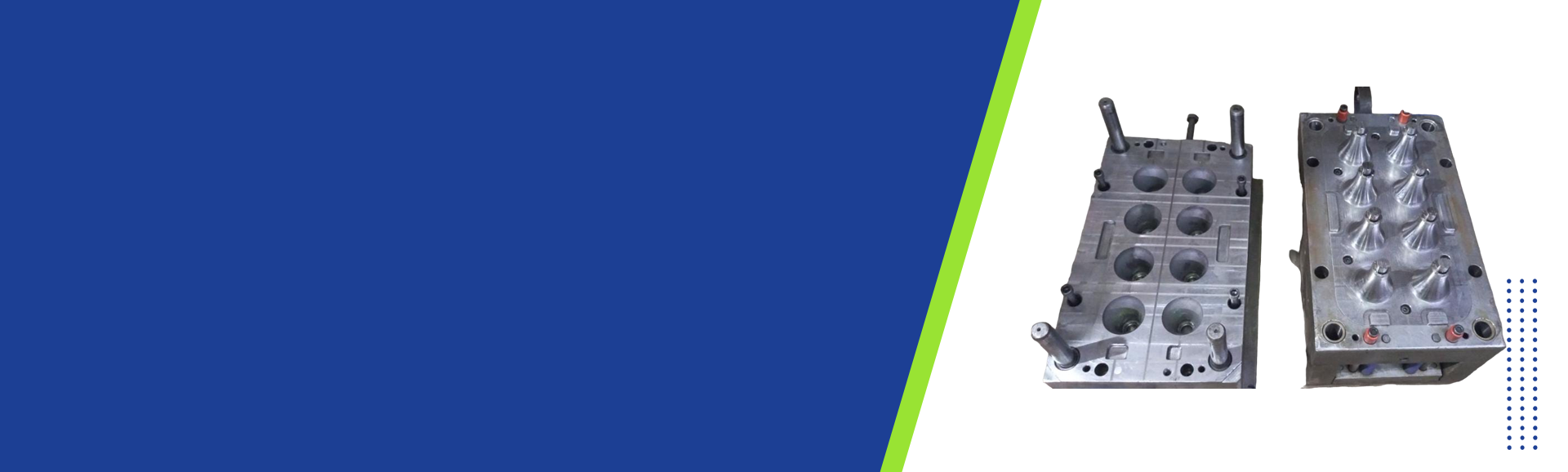
- Moulding Die
- Plastic Molding
- Plastic Injection Molding
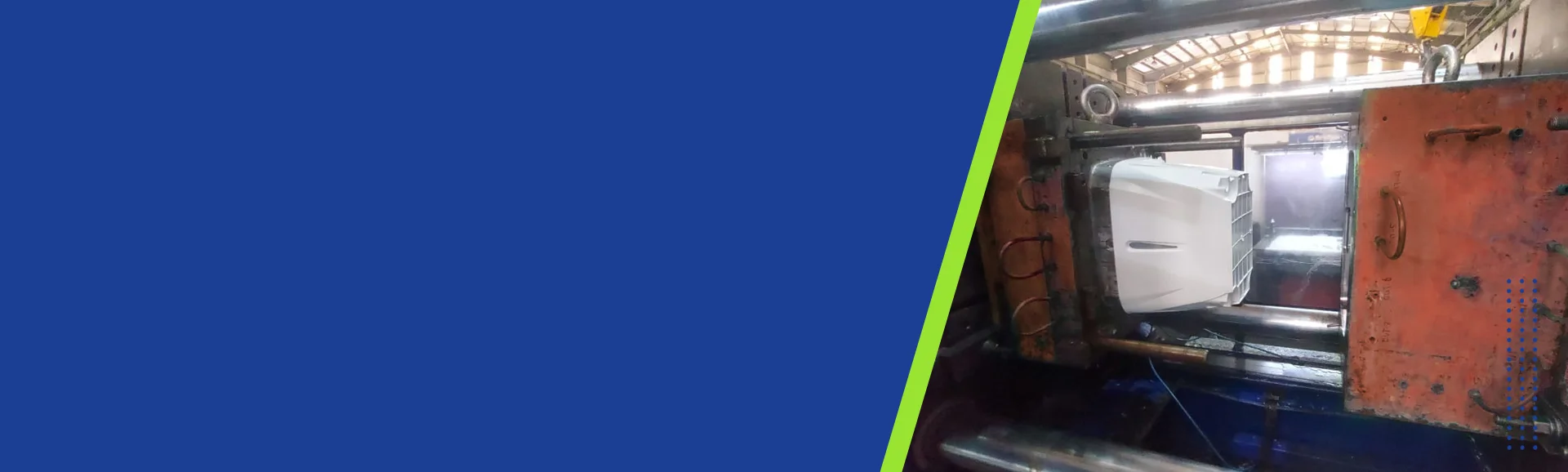
- Injection Molding
- Nylon Injection Molding
- Injection Moulding
- Custom Injection Molding
- Injection Mould
- Injection Mouldings Process Manufacturers
- Medical Injection Molding
- Polycarbonate Injection Moulding
- Rapid Injection Moulding
- Injection Molds
- Injection Molding Cost
- Injection Molding Suppliers
- Injection Moldings
- HDPE Molding
- Metal Injection Molding
- Rubber Injection Molding
- Mold Designing
- Prototyping
- Automotive Injection Molding
- Blow Molding
- 3D Printing
CAD For 3D Printing: Building The Best Prototype
3D printing is fast becoming one of the most popular options in the manufacturing industry. Regardless of the size and shape of the facility, it can be used to build finished products and prototypes. Amongst the most popular 3D printing processes, the CAD or computer-aided design is well-known. The companies in the manufacturing sector must prepare a digital design of the object using a computer. To know more about CAD for 3D printing, you need to know it inside out.
- CAD helps in designing objects using software and the manufacturing companies choose from various options to design the prototypes and products.
- The manufacturing companies use CAD software to design three-dimensional models of objects in accurate shapes and sizes.
Best CAD for 3D printing: choose the best
Most 3D printing processes require CAD software as it provides the instructions needed to create the product or the prototype. The 3D printers create 3D-printed objects through material deposition on a substrate and contains nozzle connected with the filament of the material. The material extrudes the nozzle on to the print bed. Once the base is completed, the 3D printer goes on to print the next layer. Usually, the 3D printers follow the instructions present in the CAD file.
So, you need to choose the best CAD for 3D printing to ensure the best outcome. Read the points below.
- The 3D printer focuses on the instruction present in the CAD file and utilizes the information contained therein.
- The information present in the file decides the amount of material to be deposited and its exact location.
- Usually, the manufacturing companies need to prepare a CAD file before depiction and design a mode of the object using software to ensure that the objects have the appropriate size.
- After the completion of the object model, you can save the CAD file and upload it on a printer for processing.
- The rinter3D prints the objects based on the instruction provided in the CAD file.
We specialize in autocad 3D printing and offer the best services to the customers. Just talk to our executives to find preferable solutions in CAD printing.
3D printing injection molds: knowing the benefits
Using 3D printing technology during the manufacturing of injection mold allow quick production of prototypes. Moreover, the prototypes are highly precise to perfect and expedite the design of the final part before mass production. Using 3D printing injection molds accelerate part prototyping and makes it possible to manufacture the molds within a few hours. Moreover, a 3D printed injection mold can be customized as quickly as possible during the process of product development. The molds created using ABS material makes them microscopically precise ad reduce the cost and time with faster delivery periods.
Get in touch with us for 3D printing and manufacturing services today.
FAQ
- Q1. What Are Some Practical Uses Of 3D Printing?
3D printing has a wide range of practical applications across various industries and fields. Some common uses include:
- Prototyping: Companies use 3D printing to create prototypes of products before mass production, allowing for quick iterations and cost-effective testing.
- Manufacturing: 3D printing enables the production of complex geometries and customized parts that are difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
- Medical Applications: 3D printing is used in healthcare for creating patient-specific implants, prosthetics, surgical guides, and anatomical models for surgical planning and training.
- Education: 3D printing is increasingly used in educational settings to teach concepts in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) subjects and to provide hands-on learning experiences.
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and engineers utilize 3D printing to create scale models of buildings and structures, as well as to produce custom architectural elements.
- Automotive and Aerospace: The automotive and aerospace industries use 3D printing for rapid prototyping, producing lightweight components, and manufacturing parts with complex geometries.
- Consumer Goods: 3D printing allows for the customization of consumer products such as jewelry, fashion accessories, and home decor items.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers use 3D printing to bring their creative visions to life, whether it's sculptural pieces, intricate jewelry, or innovative product designs.
These are just a few examples of the practical applications of 3D printing, and the technology continues to evolve, opening up new possibilities in various fields.
- Q2. What Is The Minimum Required Thickness?
Most processes require a minimum thickness of .025 to .030”.
- Q3. What Tolerances Are 3D Printers Capable Of Holding?
Tolerances are a function of the process and the overall size of the part.






.webp)

